The layouts of many different email clients differ. The way they should be put up, though, is the same. The settings described in this article are suitable for any client and device, including laptops, desktops, and mobile phones.
You can configure your email using one of two methods, with the SSL being the primary difference. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a cryptographic system that safeguards the communications of a computer network. SSL is frequently used to protect email, instant messaging, and VoIP systems. It’s no surprise that the two sorts of email account configuration settings revolve around whether or not SSL is utilized, given how widely it’s used in email apps.
Here are the two sorts of email configurations:
Email Settings That Aren’t Secure (Non-SSL) – Not Recommended.
Your email account on the incoming and outgoing server should be formatted as mail.example.com for non-SSL setups. Your username should be your complete email address, and your password should be the same as your email account’s password.
POP3 110 or IMAP 143 should be the incoming port. Port 25 should be used by the outgoing mail server (SMTP). Because these settings don’t contain SSL, it’s disabled. For SMTP, you’ll need to authenticate. Secure Authentication, often known as SPA, must be turned off.
SSL Email Configuration – Recommendation
For SSL email settings, the income and outgoing servers should be in the same format as the non-SSL email settings. The username and password are the same. The incoming port is the difference between the two sorts of settings. The incoming port for SSL email settings should be POP3 995 or IMAP 993. Port 465 should be used by the outgoing mail server or SMTP.
SSL is included in these settings, and it is turned on. SMTP Authentication is required, and the SPA or Secure Authentication must be off, just as it is with non-SSL email settings.
The cPanel Method
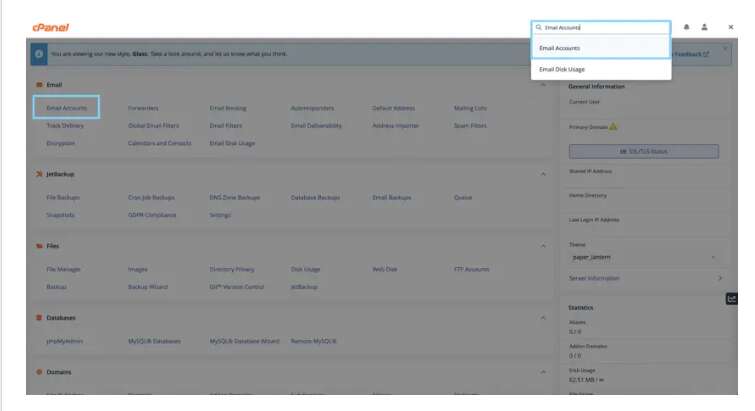
Another option is to use your cPanel account to set up your email account and obtain these settings. This can be accomplished by first logging into the account. After that, you can either type “Email Accounts” into the search field or manually search for it. After you’ve found it, you’ll notice an option for connecting devices next to your email account, which will display this information, as well as other related and useful data.
It’s critical to understand that SSL certificates based on SNI can cause issues in some older email clients. This means that instead of mail.[yourdomain.com], the incoming and outgoing server hostnames should be mail.[yourdomain.com]. Customer service will assist you if you have any problems.